If you’re a trader, then you can encounter quite a wide variety of existing markets. This is normal; after all, the vast landscape is one of the things that makes trading and investing interesting and provides great potential. In this article we’re planning to take a closer look at the spot market, cover what it is, and explain how it works.
- What is a Spot Market?
- How Do Spot Markets Work?
- Spot Price
- Assets Traded on Spot Markets
- Spot Markets Features
- Trading Mechanism
- The Types of Trading Markets
- Over-the-Counter (OTC)
- Organized Exchange Market
- An Example of a Spot Market
- Risk Management on Spot Markets
- Pros and Cons of Spot Markets
- Frequently Asked Questions About Spot Markets
What is a Spot Market?
The difference between spot markets and others is that they’re where the assets are delivered immediately. The same goes for their settlements.
It’s like transactions being decided on the spot, hence the name. The assets include commodities, currencies (including crypto), or securities. Some stock markets are spot ones as well.
Spot markets are often greatly affected by supply and demand forces, sometimes even more than forward and future ones. And make no mistake, immediate delivery doesn’t mean being instant: spot markets usually settle the trades within T+2 working days, meaning that in some cases, the trade will only be finalized two days later.

Image1 below shows the definition of the «spot market» term.
How Do Spot Markets Work?
There’s nothing difficult about the way they work. Buyers and sellers agree on a price, and the trade happens. Sometimes immediately, in other cases within 2 working days. The same rules and mechanisms that work for other markets apply to spot ones. And of course, the majority of exchanges and trading places are set in the online world.
Spot Price
The term simply refers to the actual price at which you can buy an asset or a commodity on the market for immediate delivery. When the market is highly liquid, there’s a possibility of the spot price changing in a quick manner. Spot rate is another way to call this price.
Assets Traded on Spot Markets
You can trade literally any asset or commodity on a spot market, apart from futures, of course. Let’s check out a list of the assets.

- Cryptocurrency.
- Fiat currency.
- Metals.
- Stocks.
- Derivatives.
- Bonds.
Spot Markets Features
Let’s take a look at some of the features of a spot market.
- Immediate delivery or settlement. It’s not always instant, and can take up to two days, which is quite fast.
- Transparent pricing. It’s incredibly easy to check the spot prices, they are accessible for everyone.
- High liquidity. This type of market usually offers quite a lot of liquidity due to their nature.
- Limited regulation. These markets are not as regulated as futures ones.
Trading Mechanism
Some of the spot markets feature a quote-driven trading mechanism with, market marks posting the bid and ask prices. This is especially true for the over-the-counter ones due to obvious reasons. More on that below.
The Types of Trading Markets
There are two main types of spot markets: the OTC ones and organized market exchanges. In the next sections, we will explain what they are in greater detail. The image 2 below explains them.
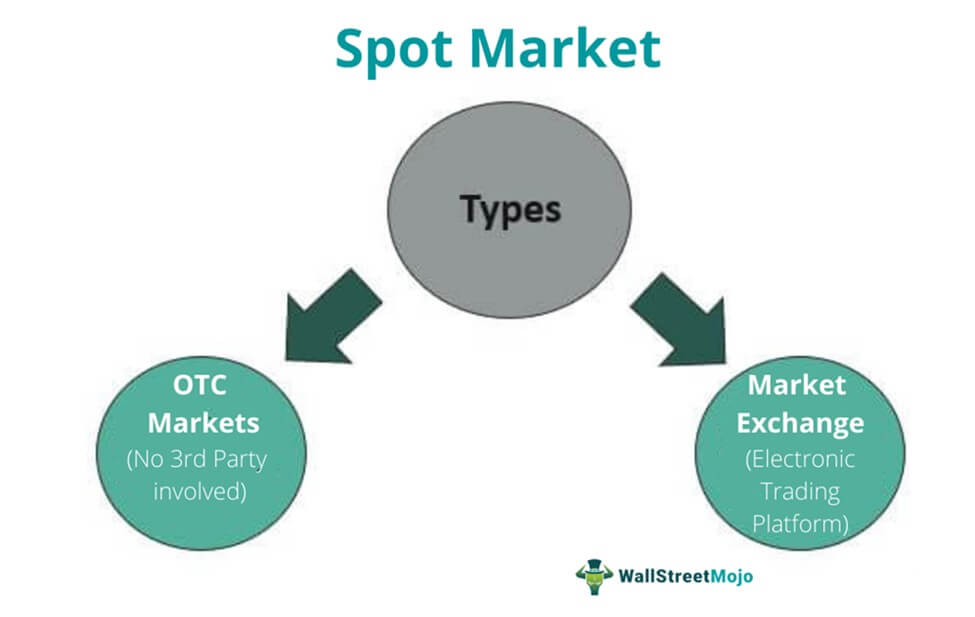
Image2. Types of spot markets.
Over-the-Counter (OTC)
These are the markets, where the trades happen directly between sellers and buyers. They might or might not follow the rules of exchanges, the conditions of contracts might be very unusual, and the price might not always be made public.
Organized Exchange Market
This is the market that completely follows the rules of an exchange that hosts it. Its main advantages over the OTC markets are price transparency, straightforward regulation, and standardization, and often better risk management.
An Example of a Spot Market
The foreign exchange market is so far the biggest spot market. It’s the place where foreign currencies are immediately traded. It’s also the biggest OTC market out there. The New York Stock Exchange is another spot market that’s widely famous and extremely popular.

You can see the logo of the New York Stock Exchange in the image3 below.
Risk Management on Spot Markets
There are certain risk management tools that the markets often utilize. Usually, the organized exchanges are better at that compared to OTC markets, but the exceptions exist. Here’s the list of some of the risk management tools and strategies.
- Margin Requirements. This is the percentage that the trader has to pay for with their own cash.
- Position Limits. This is a limitation on how many assets a trader can own.
While both tools put some limits, they also provide a lot of risk-reducing effects, making using them quite worthy.
Pros and Cons of Spot Markets
As any type of a market, a spot one comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. That’s to be expected. Let’s check out existing pros and cons of spot markets. We will start with the benefits:
- price transparency;
- high liquidity;
- fast settlement;
- active markets.

And here are the downsides:
- high volatility;
- limited flexibility;
- high transaction funds;
- impossible for hedging.
Frequently Asked Questions About Spot Markets
- What is a spot market?
A spot market involves all assets or commodities being settled immediately or within a couple of days at maximum.
- What are some examples of spot markets?
Forex and the New York Stock Exchange are good examples.
- What is the difference between spot and forward markets?
The time it takes to settle a trade is the main difference: it happens immediately in spot markets, and the forward ones involve settling on a future date.

- What’s the difference between spot and future markets?
Yet again, the difference mainly lies in the settlement time, with future markets focusing on contracts being delivered on a certain date in the future. Moreover, futures are more standardized, with the contracts following a certain set of rules. The spot market is much more flexible in that regard.