In the world of trading, margins come in different shapes and sizes. This is affected by certain formulas and the purposes of such deposits. Initial margins are probably the most common type of them all.

And in this article we’re planning to check out how exactly it works. We will take a look at the differences between initial and maintenance margin, provide some examples and even explain how the margin works for the future.
What is Initial Margin?
Initial margin is the sum that a trader places for the brokerage as a deposit. It essentially functions as a way to compensate for possible losses. The margin can be held in different types of possible assets, depending on the market. It can be nearly anything: from securities to cryptocurrencies to stocks.

The image below shows the definition of the initial margin.
How Does an Initial Margin Work?
As we have already stated, the main purpose of the initial margin is to ensure that the investor owns enough funds to cover potential losses. This means that it essentially acts as a way to secure the issues that might arise. In its essence, the initial margin acts like a deposit.

The value of the initial margin is calculated as a percentage of the overall sum, but the formula includes other factors and the exact amount depends on the brokerage, as well as a type of the margin.
An Example of an Initial Margin
Let’s say you want to buy $10,000 worth of stock on margin. The broker’s requirement is 50%. It means you would need to deposit $5,000 in cash to open the position, and the broker would lend you the remaining $5,000 to purchase the stock. Such a requirement ensures that you have enough equity in the account to cover potential losses and acts as a form of collateral for the loan provided by the broker.
Initial Margin and Maintenance Margin: a Comparison Table
There are serious differences between initial and maintenance margins. They mainly lie in the fact that the latter is required if the trader wants to continue holding the position. Sometimes, they may receive the margin call, which will require them to either sell some of the assets or increase the amount held as the deposit. The table below will provide the information about the differences between these two margin types.
| Initial Margin | Maintenance Margin |
| It’s the amount of money required for opening a new position | This sum may need to be added later and also in some cases might have to be increased after receiving a margin call |
| It’s calculated as a percentage of a total position’s value at the time of opening | It’s also a percentage of the total value of the position but it may require some adjustments |
| it can’t trigger a margin call after depositing | One may receive a margin call and will have to adjust the position |
As you can see, the differences are significant in some cases, although technically a margin is still a deposit that’s calculated as a percentage of the position’s value.
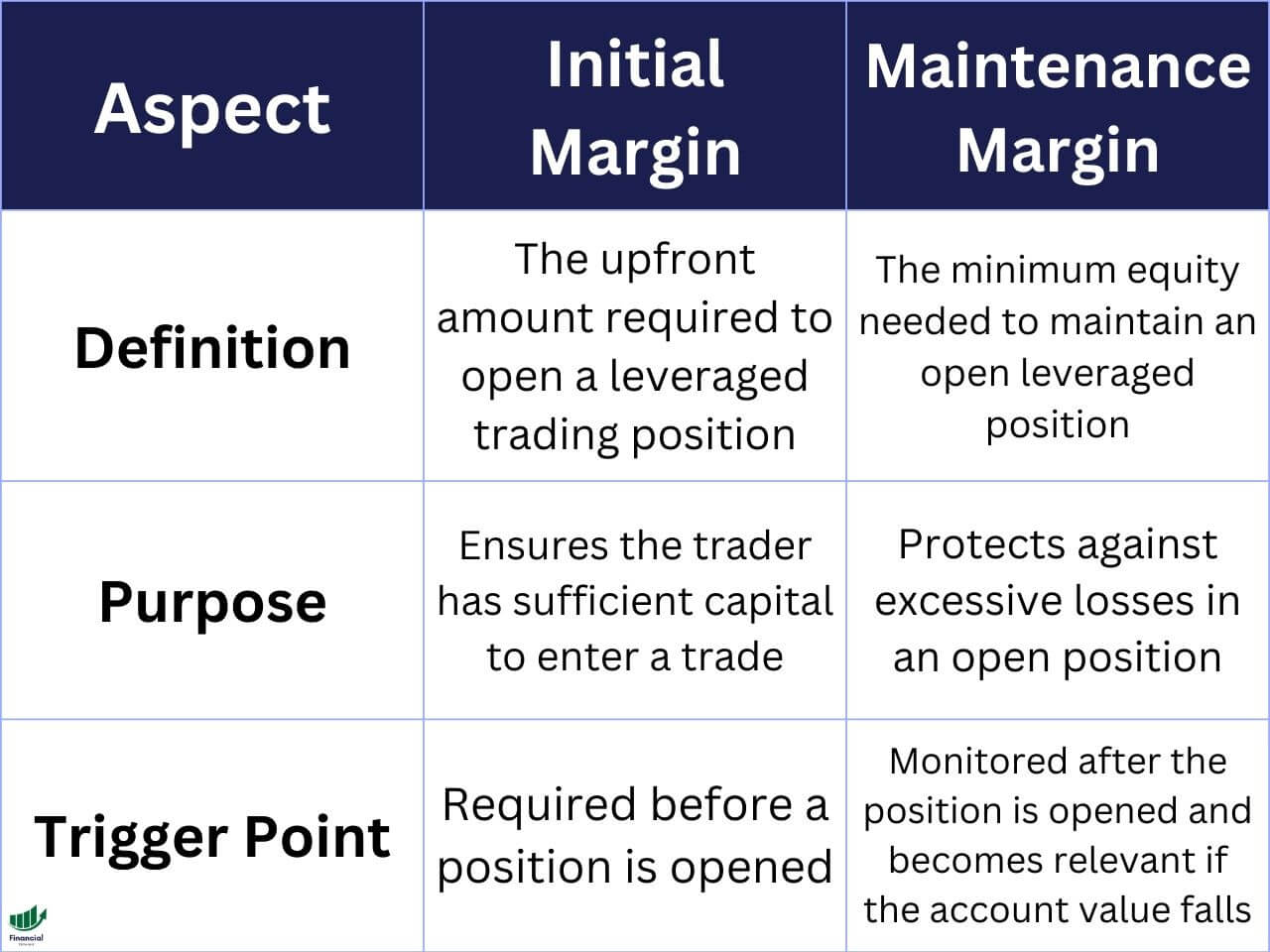
The Image below also serves as a great demonstrative table that shows the differences between the initial and maintenance margins.
Futures and Initial Margin
The initial margin exists in the world of futures. When making such a contract, one has to deposit a certain sum required by the brokerage.
Still, there are things that make it stand out. First things first, for the futures, the initial margin acts more like a deposit instead of a sum borrowed from a brokerage, which would be the case for the stocks. Secondly, the initial margin is usually much smaller for the futures, averaging somewhere between 3-12% in the majority of cases, while for the stocks it’s usually around 50%.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the size of the initial margin for futures?
It’s between 3% and 12% on average, which is much smaller compared to the stocks’ initial margin.
- What are the examples of the initial margin?
Let’s say a trader wants to buy $20,000 worth of stock on margin with a 40% initial margin requirement. In this case, they would need to deposit $8,000 in cash (40% of $20,000), and the broker would lend you the remaining $12,000.

- What is the purpose of the initial margin?
It acts as the protection for both the investor and the broker from potential losses due to market fluctuations. By requiring investors to put up a certain percentage of the total value of the investment as initial margin, the broker ensures that the investor has some skin in the game and can cover potential losses if the value of the investment gets smaller.











