A “pip” is the unit used to express the change in value between two currencies. For most pairs, a pip represents the last decimal place of the price quote.

“Pip”, short for percentage in point or price interest point, is how one measure the smallest movements in the market. In most pairs, you’ll see four decimal places, with each pip representing 0.0001.
But, well, there’s also Japanese Yen pairs, which use only two decimal places where a pip is equal to 0.01.
Anyways, we’re going to talk a little bit more about this a little bit later on, so read on!
Why use pips at all
The sheer volume and liquidity of markets necessitate precise measurements for transactions. This precision often demands a high level of decimal accuracy to capture the minute variations in exchange rates.
While pips are generally suitable, they become ineffective during periods of hyperinflation. So, hyperinflation, with its rapid and uncontrolled price increases, leads to dramatic fluctuations in currency values that pips lose their ability to accurately represent exchange rate changes. The case of Zimbabwe in 2008, where monthly inflation surpassed 80 billion percent, provides a powerful example of how hyperinflation renders pips useless due to the massive devaluation of currency.
How to calculate them
The pip, that seemingly minuscule unit, isn’t really anything of that. Like, when the dollar stands as the quote currency, the pip assumes a steadfast form – a 0.0001. Yet, when the dollar shifts to the role of base, its value becomes a more intricate equation.
The Japanese Yen, however, plays by its own rules. Here, pip’s value is sculpted from the ratio of one hundredth, then further refined by division by the exchange rate. But do remember that the value isn’t fixed; it’s rather influenced by the pair being traded, the current exchange rate, and the size of the trade at all.

Incidentally, we should note that today it makes little sense to calculate all this manually. It is a waste of valuable time. In fact, it’s much better to use special instruments, as there’s no shortage of them. And they all work on a similar basis, so you won’t really notice any particular difference.
And there is also something called pyramiding. Although it’s not directly related to today’s topic, it’s still partially related. Pyramiding is an investment strategy in which a trader gradually increases the size of his position as profits increase.
The essence is that this very trader adds new positions to those already open in case the market moves in his favor. In fact, these positions can be ordinary pips. And that’s the point. They are also statistically used more often than any other size or volume.
Are there any downsides to working with pips?
As such, no. However, it’s worth noting that working with pips can (in a most banal sense) just overload a person.
Sure thing, this can (and probably should) be controlled.
Are there any strategies related to pips?
Actually, yes. For example, the so-called “50 or 30 pips per day”.
This strategy targets short-term, intraday profits by actively engaging in multiple trades throughout a single day. And unlike long-term investing, where positions are held for extended periods, this one is specifically designed for those who seek to capitalize on immediate movements. Thus, the core objective is to capture a minimum of 50 pips. Or 30. It depends.
FAQ
What is the difference between pips and pipettes?
Within the pip, there’s a tenth of it as well, called the “pipette”.
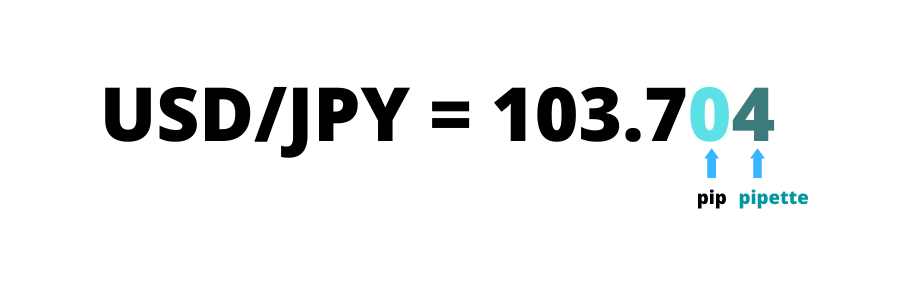
The thing is, most of the currency pairings are calculated to the fifth decimal place, which is almost molecular level. But with Japanese Yen pairings, for example, this is slightly coarser, resolving to the third decimal.
What is the spread in the Forex market?
The spread is the difference between the bid price and the ask price in Forex pairs. So, in the local market, the spread makes up most of the profit a broker charges a client for trading there.
Should be noted that there are several types of spreads in Forex: fixed, fixed with expansion and floating one.
What is a pips calculator?
The pip calculator is a tool that helps traders calculate the cost per pip in a particular trading pair and the potential profit or loss from that very trade. The calculator takes into account the following factors: the currency pair, the lot size (standard, mini, micro), the exchange rate (current or desired) and the account currency (i.e. the currency in which the trading account is held at all).

Based on this data, the calculator determines the cost per pip (how much money you will make or lose if the price changes by 1 pip, that is) and the potential profit/loss (if you specify the entry price and exit price).