So, what does synthetic mean in the market: let’s find this out by defining its products and working principles. Nevertheless, we will get to the point where it would be clear: is it profitable or unprofitable.
- Synthetic cash flows & products
- Reasons behind the synthetic position’s creation
- What are the synthetic options
- Types of synthetic options
- Principles of synthetic call’s work
- Drawbacks of synthetic options
- Instance of synthetic call
- Q&A
- Vanilla option
- Time decay
- At-the-money option protection from the losses: is it permanent?
Synthetic cash flows & products
Synthetic product is a very detailed specific build which is created and established through the contract. First of all, let’s determine two types of generic securities investments:
- Profit as an income.
- Profit as a price growth.
There are several exceptional securities which can provide traders with profit from both income and price growth.

A convertible bond is a perfect example of the synthetic product. Traders who prefer stable income are interested in the opportunity of replacing the debt with a stock if its cost significantly increases. Losing a few points of the possible appreciation doesn’t stop people because of the income which covers such expenses. Companies who would like to issue debt at a lower rate are very interested in convertible bonds.
They also are customisable and the opportunity to have a principal protection only benefits in that situation. Moreover, it can offer bigger income but in exchange for a lower conversion factor. All these additional preferences motivate bondholders to invest.
In addition, there is a special situation where an investor desires to have convertible bonds for a company who hasn’t issued any of it yet. In that case, a company arranges the whole contract directly with the investor participation in order to create convertible purchasing parts. The reason behind this is simple: there is an individual demand which needs to be fulfilled by a company.
Reasons behind the synthetic position’s creation
There are several reasons of such position’s creation:
- Ability to have the same payoff with other financial tools.
- Simplification of the process. Usage of options reduces the quantity of steps you need to do. Works in both short-term and long-term conditions.
What are the synthetic options
First of all, the usage of them reduces or erases a lot of troubles compared to operations with an underlying asset. Mainly, even a potential downfall of the price can be profitable in case of synthetic options because of the expected result. Premiums work safer than the actual operations with an underlying security.
Types of synthetic options
Let’s take a look at the list of different types of such options:
- Synthetic long stock. Its working principle is based on a long call and a short put option. It can provide the same result as if it was a long-term stock investment. The visualization is below:
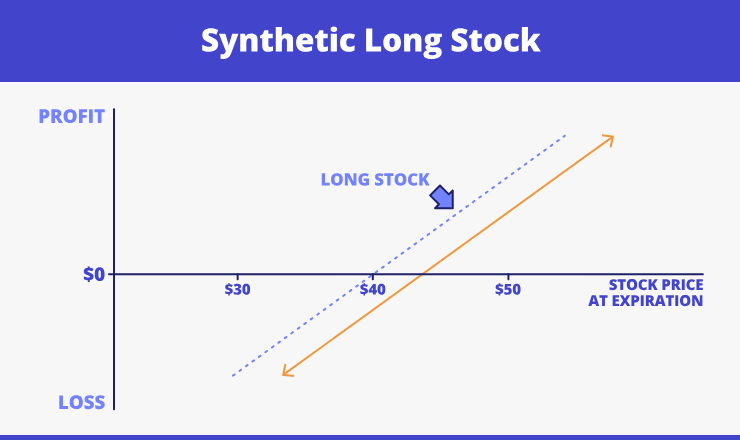
- Synthetic short stock. This type executes with a both call and put being short. It works similar to a short-term stock investment. The example on the picture below:
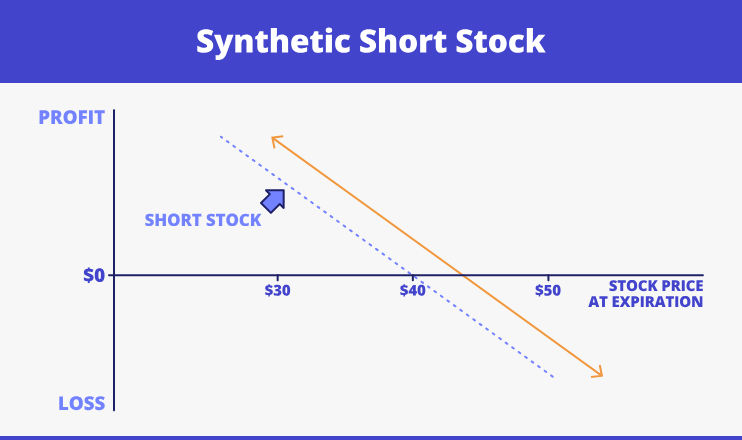
- Synthetic long call. It is based on the long put position with having the underlying security itself. Take a look at the instance:
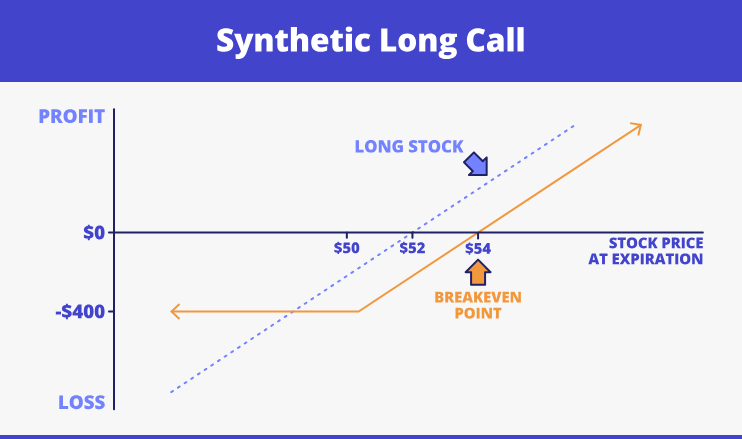
- Synthetic short call. The working principle: short sell of the actual asset and short put position. The chart below serves as the instance:
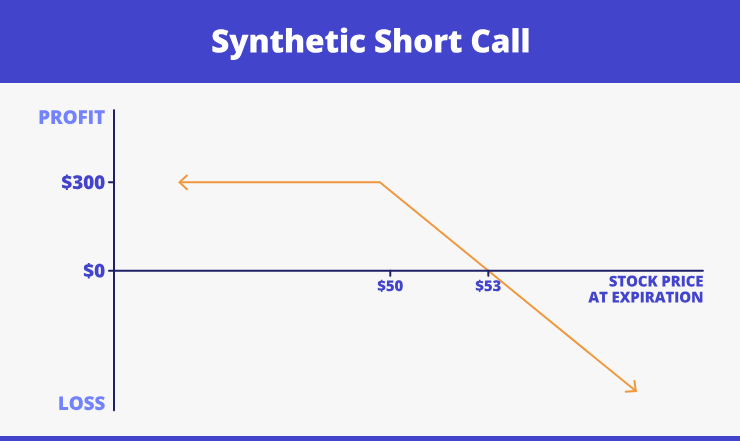
- Synthetic long put. You need to short-sell the stock and choose the long call position. Let’s take a look at the example:
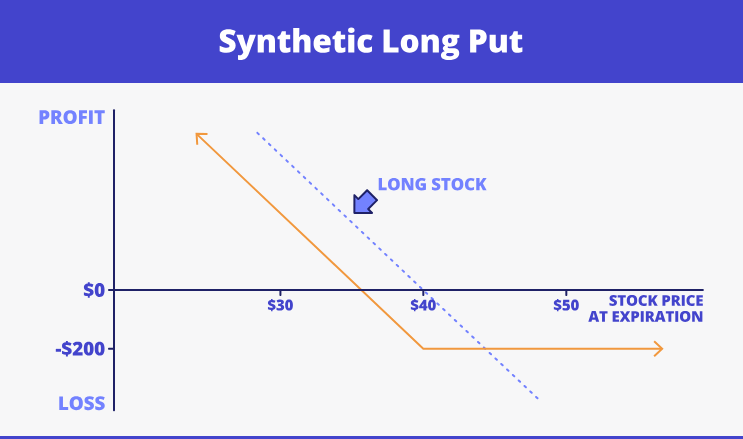
- Synthetic short put. It is about keeping the actual underlying asset and getting a short call position. This picture illustrates such an option:
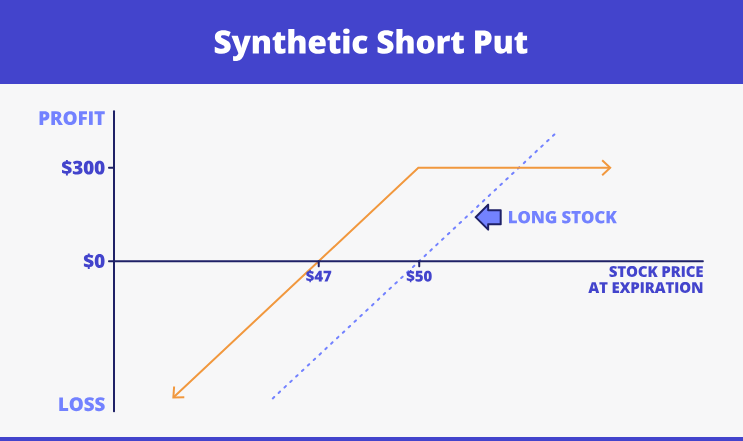
Principles of synthetic call’s work
It is also referred to as a protective call. Here’s why:
- Market player buys and keeps the chosen stock.
- Later on, he buys an at-the-money option on that asset.
All-together, such a structure creates a safety barrier which protects the investor from the possible devaluation of that specific asset’s cost.
Drawbacks of synthetic options
Even though they are an improvement of regular options, there is still a list of several drawbacks which are occurred with them:
- Losses within a cash or futures position. It can happen because of the possible market’s oppositional movement.
- Price of at-the-money options. Of course, reducing losses is important, but the cost of such protection can be high.
Instance of synthetic call
Let’s make an assumption: the cost of pineapple is at the $4.50 mark and in the current market conditions the preferable is a long-term investment.

There are two variants:
- To invest $1,200 in margin. It is definitely cheaper but the risks will be highly increased.
- To purchase a call option for $2,800. The other, but expensive way. However, it provides you with more protection from the losses.
Now, we get to the point where it’s important to decide: is it worth it?
Q&A
Vanilla option
It is based on the ability to sell and buy the underlying asset. It isn’t demanded but can be done. The cost and a deadline is decided upfront. Its name came from its basic and standard function offering.
Time decay
Time decay, also known as theta, measures the degradation of the option’s price by the time’s passage up to the expiration date. It always increases and is unavoidable.
At-the-money option protection from the losses: is it permanent?
It is not the almighty shield. First of all, a market player should consider his capital to the appetite. The understanding of the moment when you need to change a potentially losing synthetic position is the key to avoiding these losses. Such things can happen with at-the-money options, so patience, ability to react at the right time and money management will protect you from the mistakes.











