There are numerous instruments that allow investors to generate profits while minimizing risks. One such instrument is synthetic indices. Although this concept might seem complicated initially, it actually encapsulates a straightforward notion: crafting an index that mirrors the fluctuations across diverse financial markets, all without requiring the acquisition of tangible assets. Keep reading if you want to know how to trade synthetic indices.
- History and Fundamentals of Creating
- Contrasting Synthetic and Traditional Indices
- Key Characteristics
- Illustrative Cases
- Risks and Considerations
- Excessive Dependence on Algorithmic Factors Determining Price
- Importance of Understanding Underlying Assets
- Role of Brokers and Service Providers in Pricing and Integrity
- How to Start Trading
- Setting Up a Trading Plan
- Using Demo Accounts
- Advantages of Trading
- Challenges in Trading
- Questions and Answers
- How can I determine the most favorable time for trading?
- Can I trade synthetic indices/volatility indices on MetaTrader 4?
History and Fundamentals of Creating
A synthetic index is a versatile financial instrument designed to replicate the performance of a tailored selection of assets, encompassing securities such as stocks, bonds, foreign exchange, and commodities, without necessitating direct ownership of these underlying components. Its construction involves leveraging derivative tools, notably futures contracts, options, and Contracts for Difference (CFDs).

By employing these derivatives, those instruments empower market participants to capitalize on fluctuations in the collective value of the specified asset portfolio, circumventing the requirement for outright purchases. For instance, a synthetic index tracking the energy sector could include a mix of oil futures, gas options, and renewable energy CFDs, providing exposure to the entire sector without individual asset acquisitions.
This mechanism not only simplifies investment processes but also reduces transaction costs and enhances accessibility for a broad range of investors.
Contrasting Synthetic and Traditional Indices
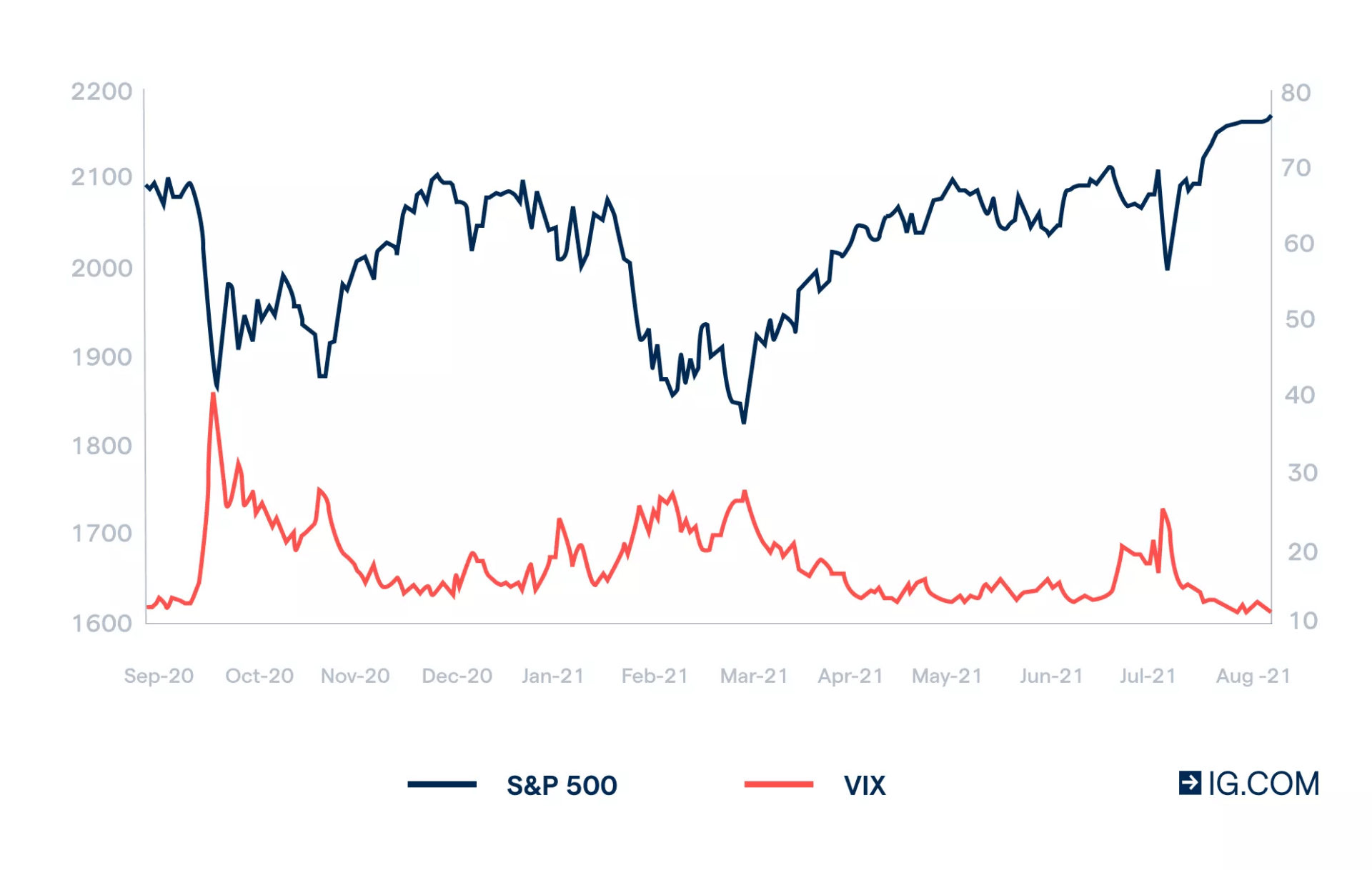
Traditional stock indices, such as the S&P 500 or the Dow Jones Industrial Average, are based on a real set of company stocks included in their composition. The value of a traditional index depends solely on the price fluctuations of the stocks it includes. In contrast, synthetic indices can incorporate diverse assets and use sophisticated algorithms to calculate their value. This allows for creating that reflect economic conditions, industrial sectors, or even specific groups of goods.
Key Characteristics
Let’s take a closer look at the key characteristics.
- Flexibility: Ability to combine different asset classes within one index.
- Absence of Physical Assets: No need to buy actual assets to participate in trading.
- Algorithmic Management: Often uses complex mathematical models to determine index dynamics.
- Accessibility: Trading is available through online platforms and brokers.
These characteristics make it an attractive tool for investors seeking to diversify their investments and maximize profits in today’s financial markets.
Illustrative Cases
An example is the volatility index VIX, which is calculated based on the expected volatility of options on the S&P 500 index. Another example is a synthetic commodity index that includes oil, gold, silver, and other resources.
Risks and Considerations
Trading comes with its own unique features and risks that should be understood before starting:
Excessive Dependence on Algorithmic Factors Determining Price
The cost is often determined by complex algorithms that take many variables into account. These algorithms can change over time, making it difficult to predict the movement of the index.
Importance of Understanding Underlying Assets
To successfully trade, you must understand how the underlying assets that make up the index behave. For instance, if the index is based on technology company stocks, it’s crucial to follow news and events affecting this sector.
Role of Brokers and Service Providers in Pricing and Integrity
Brokers and service providers play a critical role in ensuring the accuracy and reliability of data used to calculate the value of a synthetic index.
How to Start Trading
Initiating trades involving synthetic indices begins with selecting a trustworthy broker or trading platform. First, learn how to trade synthetic indices. When making your choice, consider the following criteria:
- The broker’s licensing and regulatory compliance.
- The spread and commission rates charged.
- Whether the platform offers the specific synthetic instruments you intend to trade.
- The user-friendliness and functional capabilities of the platform’s interface.
Setting Up a Trading Plan
Before beginning live trading, it’s recommended to develop a trading plan. Define your goals, entry and exit strategies, risk management, and the amount of capital you’re willing to invest.
Using Demo Accounts
Numerous brokers provide demo accounts, enabling users to simulate trading synthetic indices without putting any real money at stake. This approach serves as an outstanding method for evaluating one’s synthetic indices trading strategy and accumulating valuable experience.
Advantages of Trading
- Diversification: Opportunity to invest in different economic sectors and asset classes simultaneously.
- Flexibility: Easy switching between various assets.
- Low Entry Barrier: Many brokers offer access to trading with small initial capital.
- High Liquidity: Some of them have high liquidity, facilitating easy entry and exit from positions.
Challenges in Trading
- Uncertainty Risk: Complex algorithms underlying some indices can make predicting their behavior challenging.
- Broker Dependency: Reliability of calculations and data accuracy depend on the chosen broker.
- Fees and Spreads: Brokers might charge high fees and offer wide spreads, reducing profitability.
Questions and Answers
How can I determine the most favorable time for trading?
The best time to trade synthetic indices hinges on several key elements, such as economic reports, seasonal patterns, and technical signals. To make informed decisions, it’s advisable to scrutinize charts, examine fundamental metrics, and leverage technical analysis techniques.
Can I trade synthetic indices/volatility indices on MetaTrader 4?
Yes, many brokers support trading via the MetaTrader 4 platform.
However, availability of specific indices may vary depending on the broker.











