Years ago, the world of cryptocurrency used to consist of Bitcoin and some other alternative coins. This is no longer the case: various tokens and blockchains serve different purposes, and there are many new features and capabilities constantly added. New currencies emerge all the time as well.
- What Are Stablecoins?
- Why You Should Know About Stablecoins
- Purposes of Stablecoins
- Types of Stablecoins
- Algorithmic
- Crypto-Backed
- Fiat-Backed
- Best Stablecoins You Should Know About
- Tether (USDT)
- USD Coin (USDC)
- Dai (DAI)
- Binance USD (BUSD)
- TrueUSD (TUSD)
- FRAX
- Pax Dollar (USDP)
- Liquity USD (LUSD)
- STASIS Euro (EURS)
- Celo Dollar (CUSD)
- Reserve (RSV)
- Original Dollar (OUSD)
- PayPal USD (PYUSD)
- Best Stablecoins: A Comparison
- How to Buy Stablecoins
- Frequently Asked Questions About Stablecoins
Stablecoins aren’t exactly new; they first appeared in 2014 and, since then, have grown significantly in popularity. They offer some things that many other cryptocurrencies fail to do; low levels of volatility are one of them. In the article below, we’re going to explain what stablecoins are, their history, and their features. We will also provide information about common types of stablecoins, as well as list the best and most interesting tokens.
What Are Stablecoins?
Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies with a value tied to any other asset, which can be a fiat currency or a commodity. The idea is to counter the volatility of the cryptocurrency market by tying it to something much more stable. It also sometimes serves additional purposes by making exchanging and trading more streamlined.
Why You Should Know About Stablecoins
Stablecoins emerged in 2014, when the world of cryptocurrency was still relatively new. The first two of them, BitUSD and NuBits, were backed by other crypto, despite being pegged to the price of USD. The first one acted essentially as a smart contract, operating on the BitShares blockchain. NuBits was based on the Bitcoin blockchain and also pegged to the USD. While both projects are still technically in existence, they lost their parity to USD years ago, trading much lower currently and failing to act as a stablecoin currently.

Tether (USDT) also appeared in 2014, but months later. It fixed some of the issues presented by BitUSD and NuBits, essentially learning from their mistakes. The thing that made it successful was being backed by an existing fiat currency, essentially a hard reserve of large amounts of American dollars. As a result, USDT is the most popular stablecoin in the world, and it has also paved the way for many others.
Purposes of Stablecoins
As we mentioned in the beginning, one of the main goals that stablecoins aim to achieve is fighting the volatility that’s very common in the world of crypto. The way it works is usually by being tied to a value of a much more stable asset, for example, a fiat currency. This, in turn, makes them a great medium of exchange, since having a relatively stable value can go a long way. Moreover, they can act as a store of value, although many will argue that in this case holding on a currency a stablecoin is pegged to can be a better option with fewer risks.
Types of Stablecoins
There are many different stablecoins and several kinds of them. They can be centralized and decentralized.
The first group implies that there’s a central authority behind a coin, like an institution: for example, Tether is a company behind USDT. On the other hand, decentralized ones are independent and exist on the blockchain. Some argue that being controlled by a central entity makes the first group more reliable but there are opposing opinions as well.
Moreover, they can also be algorithmic, cryptocurrency-collateralized or backed by fiat. There are actually many parallels to the groups we mentioned above, so it gets very interesting.In the next three sections, we’re going to explore these types and explain the differences between them.
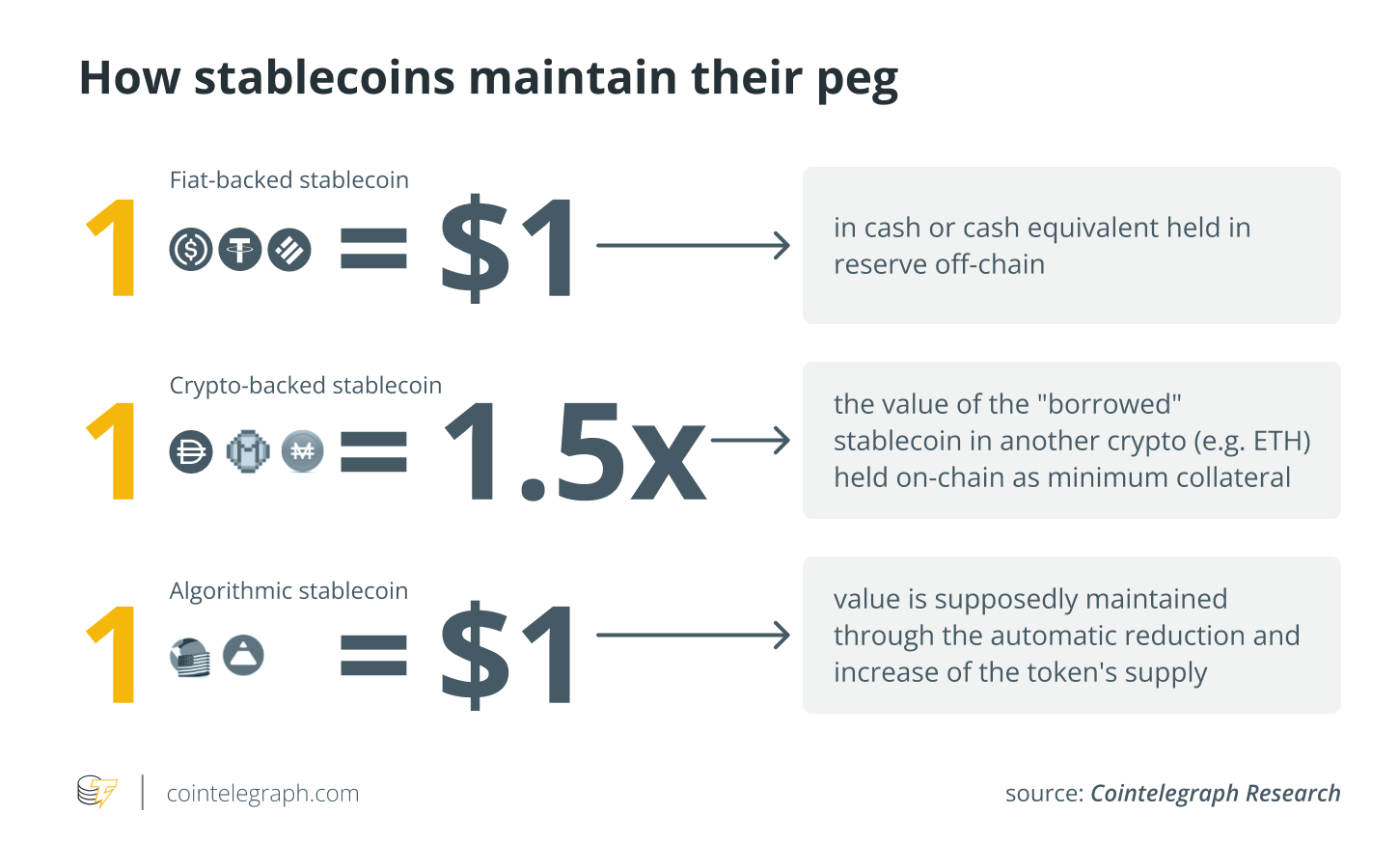
Picture below provides some basic definitions for each type of stablecoins.
Algorithmic
Let’s start with algorithmic stablecoins. They use certain algorithms to control the volatility. They mostly come in the form of smart contracts. While there are many interesting technologies used in such stablecoins, many experts criticize them as carrying more risks and volatility compared to those backed by crypto or fiat.
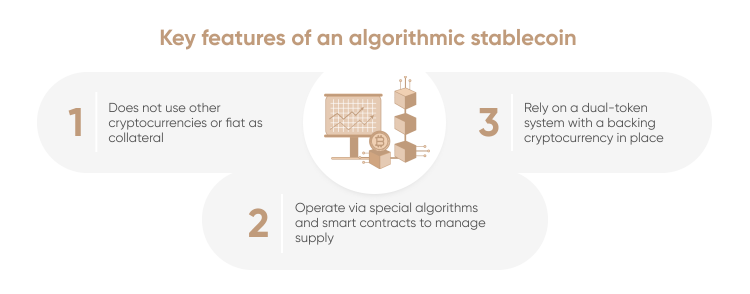
Piсture below explains some things about algorithmic stablecoins.
Crypto-Backed
This is simple: the coin is backed by cryptocurrency, while it might be pegged to any other asset, including fiat. To fight high levels of volatility, crypto-backed stablecoins use overcollateralization, meaning that there’s more than enough collateral to cover all of the potential losses. This type of currency is decentralized by design, so there’s no entity controlling it fully.
Fiat-Backed
These stablecoins are fully tethered to fiat currencies, without using any other crypto. They usually have hard reserves of this money backing them, but it’s not always the case, although it’s considered to be important. By design, these currencies are centralized, and there’s no way around it.
Best Stablecoins You Should Know About
Since the first stablecoins were launched in 2014, the world of them has become full of different tokens serving different purposes. In the previous section, we’ve already covered the main types of stablecoins, and now it’s time to move to exact currencies.
Tether (USDT)
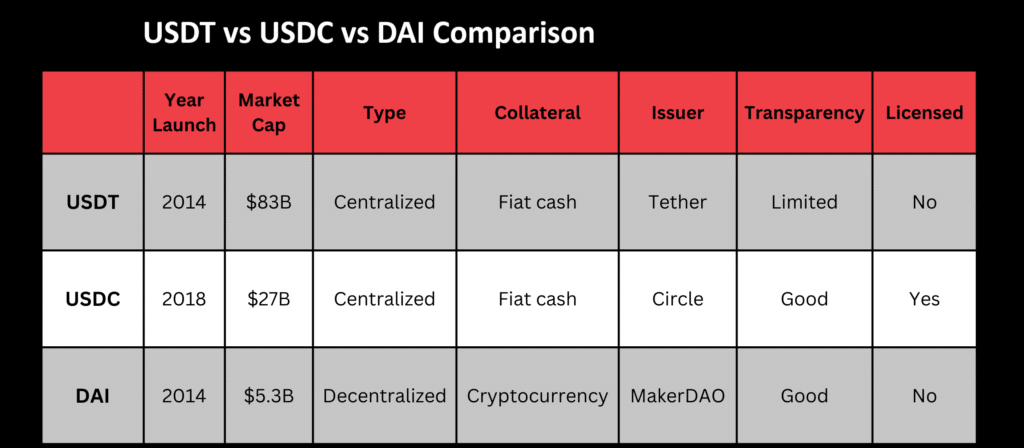
Launched in 2014 and becoming a great success, Tether (USDT) is what many stablecoins aim to be: it’s popular, actively used, doesn’t have many issues, and, in fact, stable. It’s a centralized currency and is backed by a fiat one: the American Dollar (USD).

Tether is the most traded cryptocurrency in the world, surpassing even Bitcoin (it did it in 2019). The main reason is its popularity for hedging and the fact that it makes exchanging other cryptocurrencies for fiat dollars more straightforward. Moreover, the company claims that each token is backed by an existing reserve of American dollars, but some find this claim doubtful, and Tether Ltd. failed to provide proof.
USD Coin (USDC)
Like USDT, this stablecoin is also a centralized one backed by USD. The similarities don’t end here: Circle, the company behind it, also claims to hold hard reserves of the fiat currency. This, obviously, leads to many comparisons between the two. Some consider USDC to be a more secure option, and, unlike USDT, some audits have been done, so there’s a better level of transparency.
Dai (DAI)
Dai is the first decentralized token on our list, and the most commonly used currency of this type. This stablecoin is essentially an ERC-20 token operating on the Ethereum blockchain. It’s collateral-backed, partially depending on USDC and Ethereum. The goal is to keep its value as close to the value of USD as possible.
Binance USD (BUSD)
BUSD is centralized in its nature, since it’s issued by Binance, the world’s biggest cryptocurrency exchanges. Running on the Ethereum blockchain and being collateralized by USD, it tries to keep its value very close to the latter, often succeeding.
Unfortunately, the future of this token is bleak: Binance itself announced that it will slowly and surely phase out the usage of this currency.
TrueUSD (TUSD)
TUSD is fully centralized and regulated, and, as you can already guess by its name, backed by USD on a 1:1 basis. The coin is relatively new to the market, so there’s not much feedback by its users at this moment. There’s a lot of potential to unfold, but currently it’s a bit early to tell.
FRAX
FRAX is an algorithmic and decentralized stablecoin based on the protocol of the same name. As are the majority of coins in our list, it’s pegged to USD. Locked liquidity, high level of collateralization, and being designed with stability and reliability in mind makes FRAX a coin with huge potential. And the team behind it only continues to further improve the protocol and its features.
Pax Dollar (USDP)
Run on Ethereum and Solana, this coin pegs its value to that of the U.S. dollar. The currency is centralized and issued by Paxos company, which is registered with the New York State Department of Financial Services. This makes the coin regulated, which might be a benefit for some users and a downside for others.
Liquity USD (LUSD)
This decentralized currency is pegged to a dollar value and operates exclusively on Ethereum blockchain. Liquidity is a protocol that allows investors to borrow LUSD by paying ETH. The system also has a governance token in place, called LQTY. The platform employs smart contacts which are immutable once deployed. The platform has a good reputation and useful technology behind it.
STASIS Euro (EURS)
First and only Euro-pegged stablecoin on our list, EURS is a centralized stablecoin issued by a Malta-based company STASIS. The coin meets the country’s financial standards and is regulated. The company claims that the currency is fully collateralized and backed on reserves of euros, but the reports aren’t transparent and there were no audits.
Celo Dollar (CUSD)
CUSD is the main stablecoin of Celo: the blockchain that aims to cover the needs of mobile users. The coin is fully decentralized, and so is the blockchain behind it. The developers aim to provide a great mobile-friendly user experience for those who’re planning to do payments by using this coin, and the token itself is fairly stable.
Reserve (RSV)
Reserve is a project working on an RSV stablecoin. The latter is decentralized and uses some interesting technologies, but doesn’t seem to have great parity with USD at the time of writing this article. There’s another token, Reserve Rights (RSR), that’s designed to facilitate the stability of RSV.
Original Dollar (OUSD)
Algorithmic and decentralized, this stablecoin is pegged to dollars. The developers of the protocol that the coin runs on, Origin, claim that the coin is optimized for providing maximum yield to the investors. There seems to be a lot of potential, and Origin protocol has a great reputation in the world of crypto.
PayPal USD (PYUSD)
PayPal, a globally popular payment system, announced a new addition to the world of stablecoins: PYUSD. Issued by Paxos Trust Company (yes, the same company that issues USDP), pegged to and backed by dollars, this currency might be something that will bridge the gap between the payment system and the world of crypto. There’s a lot of potential, but the coin has to prove its capabilities. Moreover, PayPal, despite its popularity, attracts a lot of criticisms.

Best Stablecoins: A Comparison
We already explained the main features of each coin. Now let’s compare them to each other in a demonstrative and accessible manner. We will do so with the help of a table that you can check out below.
| Coin | Type | Backing Type |
| USDT | Centralized | Fiat |
| USDC | Centralized | Fiat |
| DAI | Decentralized | Crypto |
| BUSD | Centralized | Fiat |
| TUSD | Centralized | Fiat |
| FRAX | Decentralized | Algorithmic |
| USDP | Centralized | Fiat |
| LUSD | Decentralized | Crypto |
| EURS | Centralized | Fiat |
| CUSD | Decentralized | Crypto |
| RSV | Decentralized | Crypto |
| OUSD | Decentralized | Algorithmic |
| PYUSD | Centralized | Fiat |
Additionally, you can take a look at Picture below which compares three most popular stablecoins against each other: USDT, USDC, and DAI.
How to Buy Stablecoins
You can buy stablecoins on centralized or decentralized exchanges with ease. Due to their low-volatile nature, the process of trading them isn’t difficult at all. Just make sure that you researched the platforms well before joining. Things to consider include their reputation, reliability, supported assets, as well as additional features. Don’t forget to look at the fees and interest rates if you’re planning to borrow the coins instead of buying.
Frequently Asked Questions About Stablecoins
- What’s a stablecoin?
A stablecoin is a token with a value that is kept as close as possible to that of some other currency.
- What stablecoin is the best?
USDC and USDT are the most popular for several reasons: they’re fairly stable, there are many coins in circulation, and the companies behind them claim that the currencies are backed by hard reserves. And Dai is the most popular one among decentralized ones.
- USDC vs. USDT: which is better?
Both are very popular, but they have their own differences. USDC is more transparent, which makes this currency more reliable in the eyes of many investors.
- What’s the best decentralized stablecoin?
DAI is the most popular choice among decentralized crypto-backed ones. It has a very reliable protocol behind it, as well as many features.











