It is crucial to understand what kind of project you enter: a possibly profitable and efficient one or a one with high risks and no possible future. That’s where tokenomics enters and guides you. Let’s review all the aspects of it to gain necessary knowledge to sort out the questions we have during the search of promising projects.
- Tokenomics definition
- Token meaning
- Coin
- Token
- Reasons behind Tokenomics importance
- Main parts of Tokenomics
- Supply
- Distribution
- Utility
- Demand
- Security
- Efficient gained knowledge
- Story of creation and performance
- Parsing and interpretation of Tokenomics
- Blockchain & Tokenomics
- Transparency
- Immutability
- Deflationary against inflationary
- Mint and burn
- Periodic releases
Tokenomics definition
As you can already get from the name, Tokenomics is an observer for a crypto token or an asset which provides investors with several important information blocks:
- Supply and future possible quantity.
- Initial distribution.
- Vesting periods.
- The utility itself.
- Mechanisms of burning.
- State within the economy.
It’s important to know that if the tokenomics of a certain token is strong, then the asset itself will be affected in a good way and improve its position within the market. In case of the opposite scenario, poor tokenomics can lead to a decrease of the price of this certain asset.

Initially, tokenomics can predict possible conditions of the observed token and help to make several trading decisions.
However, it’s not a guarantee, because there are multiple different factors which affect the token value: market sentiment, changes within regulations, wider adoption trends and tech advancements – all of it has a different, but also important influence on the token’s valuation.
Token meaning
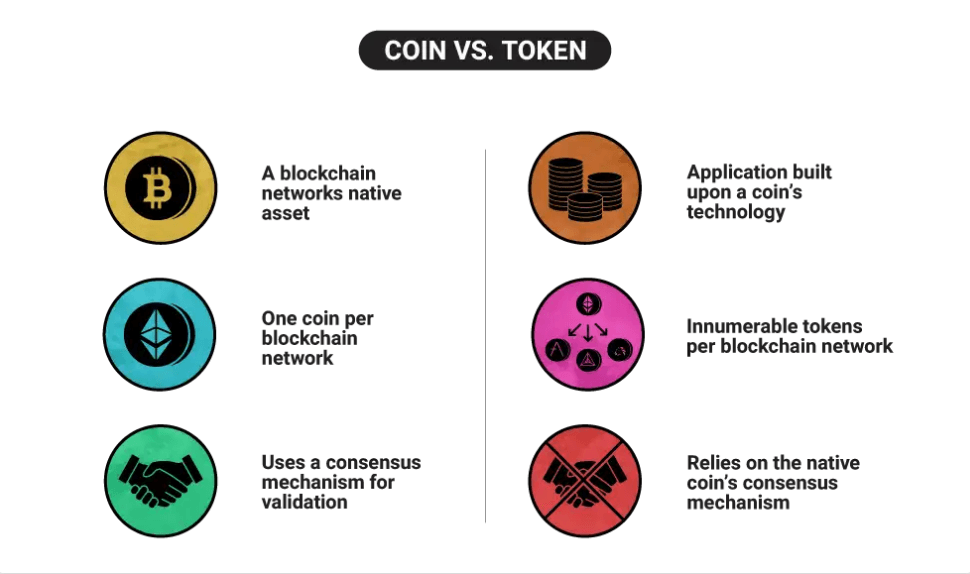
Firstly, we need to understand that tokens and coins are two different things. Indeed, they’re both digital assets within the blockchain system, but each has its individual features.
Coin
Coins are cryptos with basic and common goals: be an exchange asset, one of the ways to store funds and be a unit of account. Its flow often operates within the maternal system, like BTC, for instance, which homeland is the Bitcoin blockchain.
Token
Tokens, however, don’t have their initial separate blockchain systems. They can be created and released from a variety of platforms.

Another significant difference of token is its purpose: it can execute the role of an asset, be as a stake in several projects, become a pass for certain projects and e.t.c.
Take a look at the table of the differences between these crypto assets below:
Reasons behind Tokenomics importance
It’s great to have a knowledge of the upcoming project that is why Tokenomics is a perfect advisor and guide to the existing intel for all new and old tokens. There are several reasons why Tokenomics is that important:
- Ability to review the Token’s demand, utility and value proposition which later on can guide people to decide their future with the chosen asset.
- Overall influence on the token’s lack or plenty. Later on, it can affect the cost and adoption rate.
- Determination and description of the lock-up periods and token issuances. This feature can help you to interpret existing and future valuation movements.
- Ability to define the structure.
Main parts of Tokenomics
Every developer of the new token must prepare and build an efficient structure to release a successful project. There are several main components which directly impact its future. Let’s review each of them.

Supply
The initial supply of a token must be calculated and released in an almost perfect balance to achieve the best outcome. The system should be able to comprehend a variety of factors to execute the whole supply in the right way. There several parameters of supply which are needed to be calculated:
- Maximum supply. It’s the initial planned number of tokens which will exist. Huge part of the whole number often is held from the circulation by the developers – it’s a usual decision for most new projects.
- Circulating supply. The available crypto within the market. It can be bought or sold.
- Fixed supply. There are multiple cases when the projects mine all tokens before the planned release. The prepared number of tokens is generated before the accessibility to the community. It can be executed for several reasons: fundraising events, giving a token as a developer reward and marketing events. All what’s left will be released and distributed to people within the ecosystem of a dropped crypto.
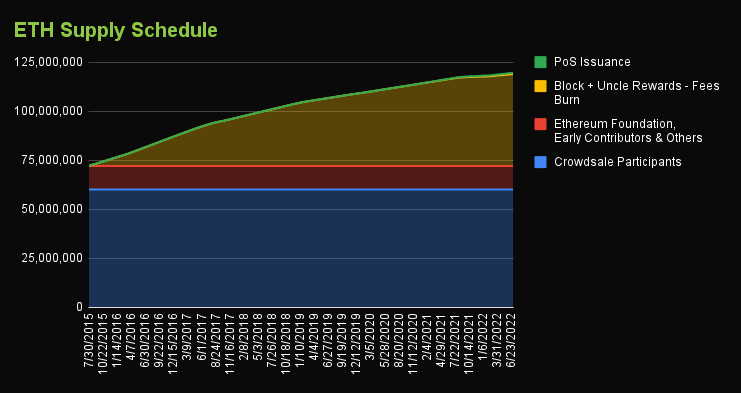
- Inflationary supply. Token is created through the smart contract which means its flexibility in the adjustment. Principles of PoW and PoS can be integrated in the contract which provides a functional system of reward.
Here’s an instance of the Etherium supply graph:
Distribution
The token technology became very innovative with all the new abilities it has.
This innovative structure and its principles provide investors with a variety of distribution ways:
- Vesting. It works like an additional bonus to gain the investor trust in a new and unreleased project. The whole process of vesting is calculated and scheduled to avoid early sell-offs which will help to gain more control of the token’s stability.
- Staking. While being staked, tokens are unavailable to the circulation flow which later on can affect the valuation in the future. Lack of that specific asset can increase the price. Several projects provide stakers with voting rights which gives them authority to impact on the given crypto’s future.
- Airdrops and other rewards. Such ‘presents’ helps to control the project popularity and visibility status. Moreover, it can directly reduce potential centralization risks in the future. It works much better in cases when the token is related to governance rights. In addition, such events decrease the risk of facing regulatory issues and increase the spreading of the project.
Utility
The utility itself is very important to make the project much more integrated in the system. That’s why there are two types of utility: good and bad. Let’s take a look at both of them and review the reasons why each one stands for specific token features.

Good utility:
- Access rights. The ability to use specific features of the platform is increasing its potential and efficiency.
- Governance. Another good feature is to have an opportunity to vote and participate in the future of the project.
- Staking and network security. The PoS systems are useful to improve security because of the ability to stake tokens as a validator of the transactions and a resource for the creation of new blocks.
- Collateral and borrowing. DeFi platforms allow people to use tokens as collateral and it gives the user an ability to borrow another asset.
- Fee reduction. Several blockchains allow users to pay a reduced transaction fee with a related token.
Take a look at several popular utility tokens with their own services:

Now let’s review bad token utility:
- Forced adoption. The unnecessary pressurised marketing of the token with an intention to sell the token or give with no obvious reason is decreasing the trust in the project. If the token is just a crypto with no certain purpose and it can be replaced and just reviews lack of utility.
- Redundant utility. If the token as a unique crypto does not classify itself for specific purposes and just repeats the existing one within the ecosystem it can decrease the valuation and retract users from usage.
- Overcomplicated utility. If the execution process with usage of a certain token is too complicated it can push away users from adopting and operating with this crypto.
Demand
It all comes from the initial market system of supply & demand. Chosen token must be efficient and useful for the stakeholders and investors to perform good enough.
There are several ways to increase the token demand:
- Clear utility and use case. The asset must be transparent with its functions to all who are interested in the project.
- Reliable technology and security. It is very important to be scalable and secure for the token to perform better, because the ability to protect an asset with a flexing structure of the execution process increases the trust in the project.
- Partnership and collaboration. It is especially crucial to take part in shared projects with existing and established partners to gain the additional trust and expand the field of usage throughout the system.
- Liquidity. Ability to trade the token with no issues and with high speed, listing on big quantities of crypto exchanges will significantly increase the popularity and trust of the potential stakeholders and investors.
- Integration and ecosystem development. Using opportunities to integrate the project on different platforms and the involvement of third-party developers significantly increase the usage field and the possible demand in the future.
Security
It is very crucial to have a strong security base for the project. The reinforced structure of the platform and the token itself increases the overall trust in it.
Pivotally, the ability to store and to provide efficient, protected and fast transactions is playing a huge role in the token’s demand around the system.
Efficient gained knowledge
All the gathering intel by tokenomics can guide users throughout the web of doubts and bad projects by evaluating the necessity and toughness of it. There are many aspects to be followed with tokenomics:
- Supply dynamics. An important data which can help to avoid any potential pump and dump schemes.
- Transparency and governance. A fair shared design of the project structure provides more trust and decreases possible schemes of manipulation.
- Utility and demand. Usefulness and good circulation of the token will give you the necessary impression of positive tendencies with it. The price of this asset is measuring the success of the developed system itself.
- Community and communication. Wide-open community and free-to-access data of the project increase the overall trust in it and helps to gain more reputation within the market. However, the balance between the popularity and multiple discussions must exist to prove the quality of the developed token.
Story of creation and performance
The birth of tokenomics happened with the release of Bitcoin (BTC), the first ever existing cryptocurrency. The white paper of the project revealed all the details and that level of transparency and simplicity of the concept had a great potential.

The principles of the structure:
- Maximum supply: 21 million coins.
- Mining principle of solving mathematical puzzles for the reward.
- Halving model: every 210,000 blocks the reward is decreased by a half. It started from 50 BTC per block, currently, it is 6.25 BTC per block.
- Transaction fees of the newly validated block. It enlarges the size of the transaction and congestion of the network.
The simplicity of the structure attracted users to participate. Later on, more projects started to appear on the market. The first blockchain systems began to form. One of these newborns was Etherium. It followed the existing pattern of the Bitcoin chain structure, but despite all the initial benefits, several issues occurred.
Large quantity of situations when the network congested under the influence of multiple transactions directly impacted on the transaction fees. Etherium suffered from this problem hugely and limited the scalability of the blockchain. It helped to avoid the falling of the project, but created a massive criticism due to decreased usage of an asset as an easy, low cost and fast payment method.
The update on September 15 of 2022, which is called The Merge, which turned staking as a primary incentive mechanism.
Parsing and interpretation of Tokenomics
It is a known fact that supply and demand are both mainly important for the cost situation of an asset. Let’s review both sides of the story.
Several factors have an influence on the cost by the supply changes, but there are two main processes which affect the most:
- Inflation. The known principle of decreasing the cost of the token by the increase of the supply.
- Deflation. The converse process of reducing the supply which makes the price rising.
Based on that, tokenomics help to observe the data about consequential changes of the supply of the desired token which helps to prepare for making any investing decisions.

Secondly, we have the demand. Right at the start of the project nobody has the knowledge of the future demand of the product or service, because you simply haven’t checked the overall behaviour of an asset within the market. Tokenomics, however, helps to understand the demand pattern: will it be high enough to participate or not. There are 3 key components you need to investigate:
- Return-on-Investment (ROI). It is an expected value that the investor could potentially gain for just holding an asset. Indeed, passive income is an attractive feature in many cases. You can gain the profit by staking it to validate transactions within the systems which use the PoS protocol. One more way to receive an income is yield farming or providing the liquidity to Decentralized Exchanges.
- Community. A very crucial factor when it comes to trust. If the community continues to discuss the project, propose changes and is actively involved in the future of it, the token’s demand will surely rise.
- Game theory. There are multiple occasions when people drop the project at the first indications of trouble. Of course, it can affect the demand, but that’s what the game theory is for: guiding a user to understand why people make certain decisions by a mathematical model. For instance, multiple projects offer you a profit for staking and holding the asset. If you hold longer – you will gain more. When the pattern is clear for the participants it motivates them to withstand and continue to store the asset. Such models can improve both utility and demand in the future if they’re executed correctly.
Blockchain & Tokenomics
Tokenomics observations have a huge impact on the investor’s decisions. There are 5 main components of the blockchain which are being reviewed by tokenomics:
Transparency
When it comes to transparency – public blockchain systems are at the top. The ability to monitor the whole activity and participate in not only simple, but very crucial events which occur on the platform is a huge incentive factor for the user to join. Moreover, the viewed activity can guide you to the safeguarding of your positions: preventing strategies which will protect your own market state.
Immutability
The structure of the blockchain provides people to participate in the future of it. The result of participants voting is the key factor of the platform decision: if users accept it – it will pass and be applied. It is a fundamental rule that even the founder himself doesn’t have a right to execute a change without the community permission.
Deflationary against inflationary
Both of these tokens move into the opposite directions of supply:
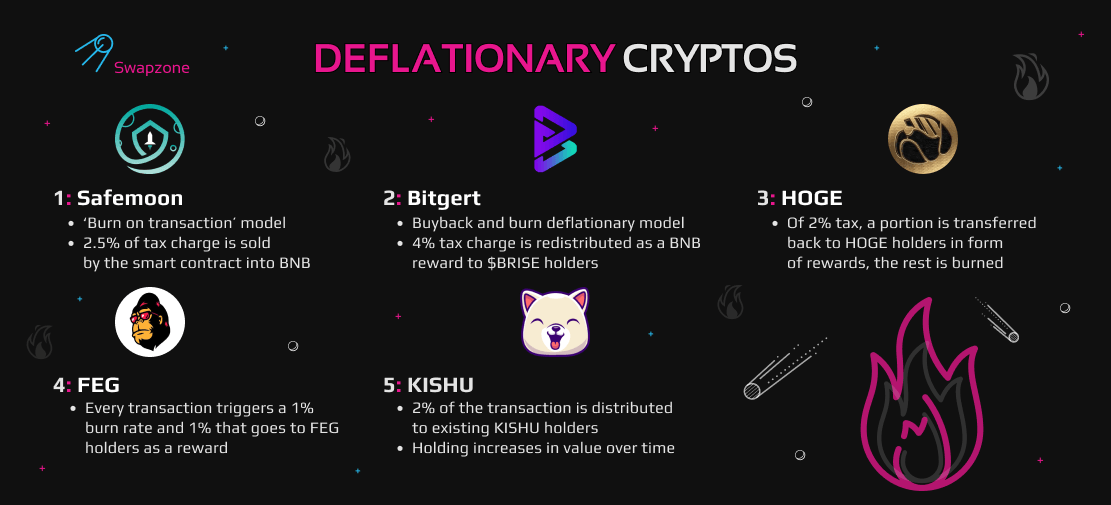
- Deflationary. The quantity of an asset is periodically decreased to help the demand to grow. The so-called “Burning” process is a perfect example of the token’s reduction process. There are several examples of this type of token below:
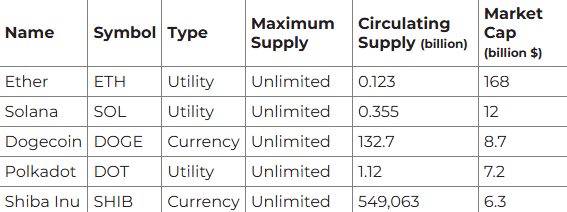
- Inflationary. The opposite story: the supply of an asset is constantly increasing to withstand pressure and assist the demand in growing.
Here’s the top 5:
Mint and burn
There are several examples of the burning, but there are cases when all the supply is minted and burned periodically due to specific patterns. For instance, Shiba Inu, which followed this strategy and half of all the tokens was burnt after the launch. The table below will show the state of the Shiba Inu supply situation:

Periodic releases
It is common to add more tokens in the circulation by the system. If the asset is proved to be efficient and usable: it needs more supply within the ecosystem. One of the most usual instances is the reward sequence for the validation through the PoS algorithms.