Any business is determined to succeed and there are many ways to enhance the profit. However, each approach fits specific conditions and that’s why the following analysis of the Operating Leverage is crucial: it will help to understand the efficiency of this enhancement and to identify fitting conditions for the tool to make the best of it.
Definition
There are two types of leverage: operating and financial. An operating one stands for the enhancement of the effect which sales changes have on the operating profit by the expense structure.

The key factor is the comparison between the fixed expenses and variable prices. The financial one is based on the increase in returns on equity which is created by debt utilization. In other words, the loan is used to gain profits by purchasing new assets with the intention to gain from it the return which is higher than the initial interest rate.
Principles of Work
There are several main features of its principles of work:
- Determining bigger change in operating income at the time of the sales evolving. It is common with the companies which have high fixed expenses which stay at their level. The additional profit is gained due to the impact of extra sales.
- Even a small amount of sales may increase gainings drastically, but the same can work on the other side: if the sales are decreasing – it may create a huge downward momentum because of the fixed expenses.
- Wise utilization of the operating leverage can be achieved by strong companies which can hold both demand and margins at the necessary high levels.
Formula
In case of operating leverage, there are, actually, multiple formulas for different occasions:

Despite the prior knowledge it may provide, it is not commonly used by many businesses due to the fact that they don’t reveal the exact value of their fixed/variable costs.

This is a widely used formula for the reviewing of a public company with a variety of information throughout the history despite the limits of the allowed disclosure. However, it is not a clear value, because it is not including only fixed and variable expenses which can lead to misguidance.
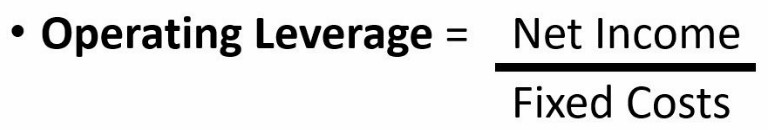
Despite not having an opportunity to calculate the value with the real existing number of the fixed costs (because of the non-disclosure position which most of the companies hold on to), this is an option if the Operating costs are equal to Fixed ones and the variable ones are the service’s price or the amount of goods sold costs.
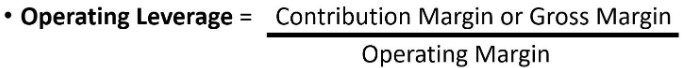
It is an essential formula of the operating leverage for the software companies: it can provide them with twice the amount of production to the amount which is produced for the company that sells its services.
Types
There are two types of the Operating Leverage:
- High. This state of the company shows that it can gain a drastic profit from the increase within the sales volume – even the small change is the case of getting an income. Conversely, the same thing could happen if the sales drop down: huge losses are the risk which accompanies the opportunities to gain profit.
- Low. The other way around is when the company has low operating leverage. Surely, there are less risks because the changes in sales won’t affect the profit margins at high levels, but that also means the overall drop of the potential gains, because there are more variable costs.
- Moderate. This is a more stable approach of the company which can be described with the following statement: the proportions of fixed and variable costs are made balanced to reduce the potential risk or make it more flexible for the actions which are directed to gain an income.
Instance
Let’s take a look at the hypothetical example of the Operating Leverage. For instance, there is a firm whose prior goal and specialization is to develop the network. It supposedly has the following fixed costs: $500,000. The next necessary value to consider is the cost of a single unit, which is $0,10. The quantity of the units which are gathered to be sold is 120,000 units at $15 per one. Let’s determine the operating leverage of the company.

By utilizing the initial formula, there is an equation to solve:
(120,000 * (15 – 0,10)) / (120,000 * (15 – 0,10) – 500,000) = 1,288 or 128,8%. After calculating this value, it is not difficult to measure the potential profit: if the sales start to increase by, for example, 20%, the profits of the firm will be increased by 25,76%.
Industries
After defining the types of the operating leverages, let’s define the companies which are commonly connected with both high and low.
High
There are several existing instances of the industries which are based on the high operating leverage:
- Mining industries.
- Utilities.
- Airline industries.

All the companies, which are matched to the definition, have a sufficient amount of fixed costs. It, consequently, may lead to several profit earnings due to the utilization of the additional funding to continue the service providing which can increase sales. For instance, if all the tickets on the airplane are bought – the company will gain from such sales, but in case of less sales, the provided fixed amount of money which was allocated to increase the sales, will be uncovered and the loss is consequential.
Low
The other example is the low operating leverage which is also is common for several industries:
- Retailing.
- Restaurant industry.
It is fully explained by the initial costs that are higher – the raw ones. The main reason for this is the necessity of the company. In the case of the restaurant business, the company may increase the amount of sales by buying more necessary ingredients to enhance the amount of food for selling. The same story happens if the retailer decides to increase the profit by raising the sales volume: he will buy the required goods for the production, which will help to enhance the production. If the business is successful, such addition will help to gain more by providing the desired product to the consumer.
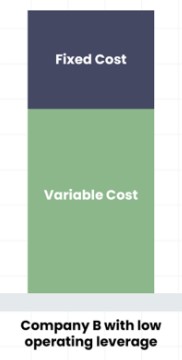
Moreover, the companies, which have a low operating leverage, don’t feel the impact of the sales increase or decrease as it would be in case of a high.
Existing Strategies
There are several ways to implement the Operating Leverage. The existing strategies are:
- Cost Structure Optimization. This is a safe way to decrease the influence of the bad situation: the company can transition fixed costs by the required amount to avoid the expected impact in the possible future.
- Predicting the sales. If the company utilizes this instrument, it also may predict the potential amount of sales in the future which helps to reconfigure the existing business model and set the expenses at the most fitting amount to endure the difficulties and profit from the opportunities.
- Diversification. More specifically, a business can adapt to the conditions by involving itself in more development which can increase or make the income more balanced and stable. This action can help to avoid the losses which can occur due to a single source of income.
However, there are many more ways to utilize it, but it all leads to the company’s type and the expected goal.
Operating vs Financial
There are several major differences between these types of leverage, let’s analyze each of them and compare. Firstly, the operating leverage:
- An operating income is raised by the fixed costs impact.
- It is a more useful tool in the hands of a stable and strong company which has a history and existing levels of demand which are continuing to evolve to the predictable pattern.
- The most disadvantageous side of it is the fixed cost inflexibility which comes with a strong margin pressure.

Secondary, the Financial Leverage:
- In this case, it enhances the return on equity by the debt.
- The peak of utilization can be reached by the promising companies with an existing potential of growth and with stable cash flows which means that the company will not lose from the loan and receive more than invested.
- However, the profit highly depends on the market sentiment and the overall economic situation together with the interest payments.
In other words, both of the leverage types are useful, but in different circumstances that may occur to the companies. The choice fully depends on the type of business and the approach it has.
FAQ
What is Operating Leverage?
It stands for the enhancement of the effect which sales changes have on the operating profit by the expense structure. The key factor is the comparison between the fixed expenses and variable prices.
How to calculate an Operative Leverage?
There is a common formula: % Δ in Operating Income ÷ % Δ in Revenue.
What’s the difference between the Financial & Operating Leverage?
Both of the leverage types are useful, but in different circumstances that may occur to the companies. A Financial one uses debt to increase the return on equity, an Operating one moves towards the direction of the operating income increase by the fixed cost influence.











